How to create and download website backup automatically
- Category : Tips and Tricks
- Posted on : Aug 19, 2020
- Views : 1,991
- By : HostSEO

To automatically create a backup of the website(s) hosted in your account, you can take advantage of various tools which Linux systems provide. In order to be able to set up automatic backups, it is necessary to have:
- Shell access enabled for your account;
- Key-based authentication configured â$“ your key should not have a passphrase.
This article is for the following scenario:
1. You are backing up a single website, which is located in the /public_html directory of your account.
2. The website uses a database.
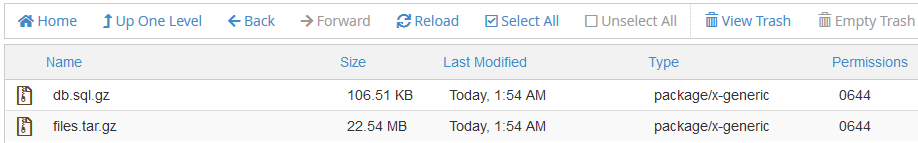
3. A folder will be created for each backup. Two files db.sql and files.tar.gz will be created inside the folder.
4. The backup file will be generated on the server and downloaded to your local machine using scp.
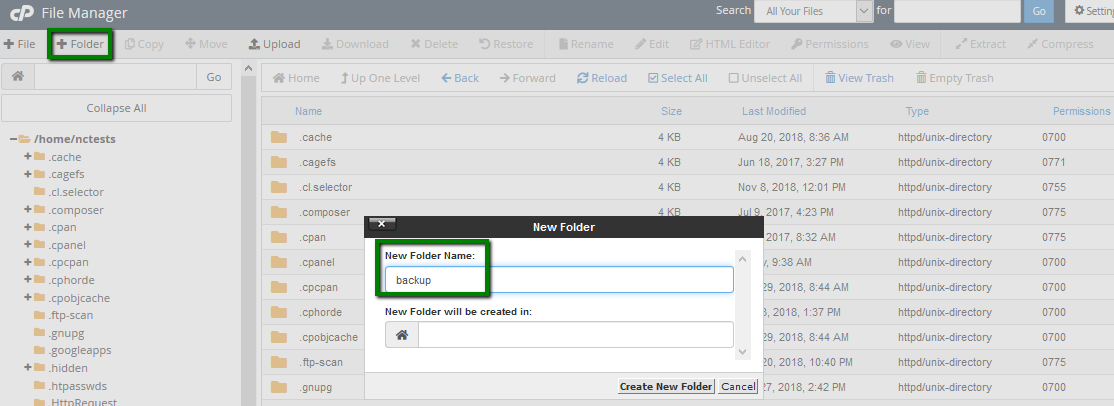
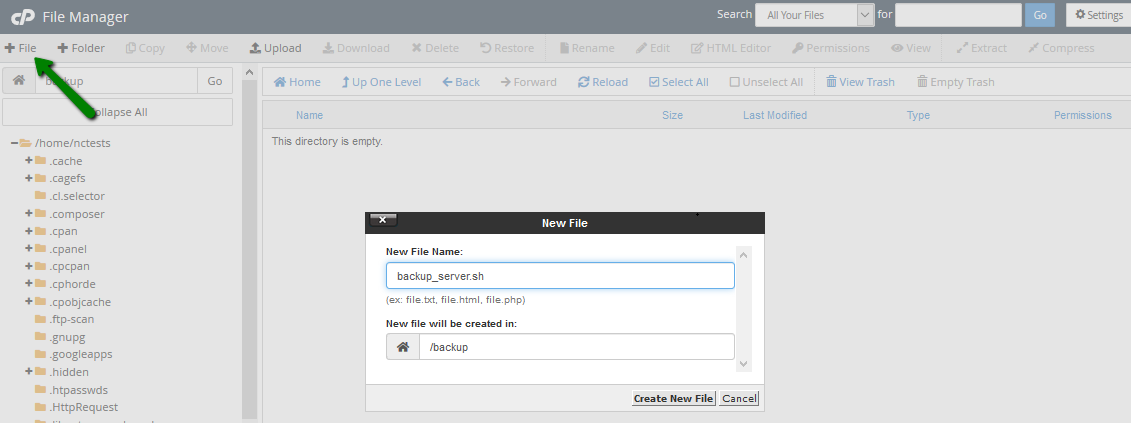
Once done, Edit the backup_server.sh file and paste the following code inside:
#!/usr/bin/env bash NAMEDATE=`date +%F_%H-%M_%s`_`whoami` mkdir ~/backup/$NAMEDATE -m 0755 mysqldump -u dbusername -p"dbpassword" dbname | gzip > ~/backup/$NAMEDATE/db.sql.gz tar czf ~/backup/$NAMEDATE/files.tar.gz ~/public_html chmod -R 0644 ~/backup/$NAMEDATE/* exit 0
The database parameters are to be adjusted, namely:
- Replace dbusername with the actual database username (weâ$™ve used nctest_production as an example). This can be checked in your websiteâ$™s config file or in the MySQL Databases menu.
- Replace dbpassword with the actual password for the selected database user. Note that there is no space between -p and the password itself.
- Replace dbname with the name of the database.
You can also use the absolute paths (e.g., /home/username/â$¦), specifying a different directory to be backed up and/or a different one to store your backups. Donâ$™t forget to double-check if all the paths are correct.
Once you have edited the file to have the correct parameters, save it:
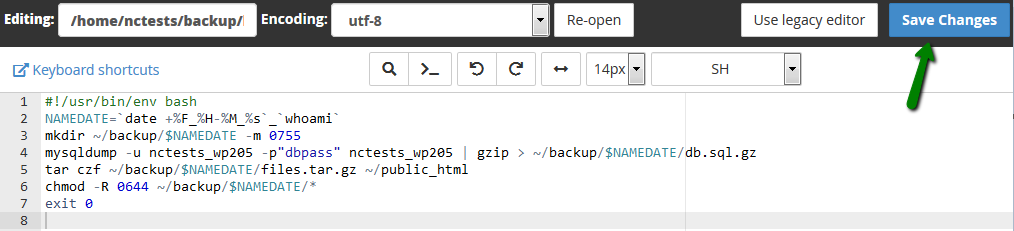
- Minute: 30
- Hour: 0
- Day: *
- Month: *
- Weekday: 1,4
- Command:
/bin/bash ~/backup/backup_server.sh 2>&1
With these settings, the backups will be created at 12:30 AM EDT every Monday and Thursday.
Minute, Hour, Day, Month, and Weekday can be adjusted according to your needs.
Do not forget to change the script path in the Command line if youâ$™ve placed it in a different folder and/or under a different name.
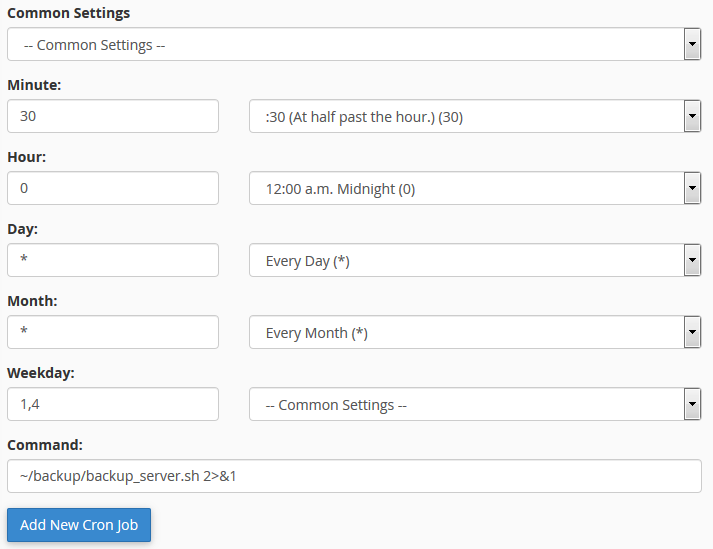
The folder contains two .qz files inside - the backups of the website files and database.
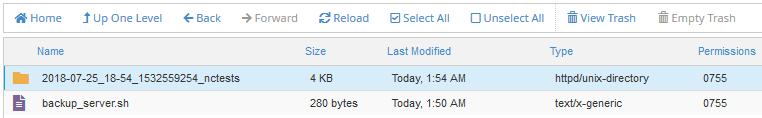
- Minute: 0
- Hour: 0
- Day: *
- Month: *
- Weekday: 0
- Command:
cd ~/backup; find . -type d -mtime +7 -exec rm -rf {} \; 2>&1
This job will run every Sunday at midnight EDT and will remove all backups older than 7 days. You can adjust these settings according to your needs.
1. Connect to your account via SSH (for macOS). Start with creating the folder which will store your backups. To do this, run these commands one by one:
mkdir ~/backup touch ~/backup/backup_server.sh
2. The file must be executable, so donâ$™t forget to set the permissions:
chmod 0755 ~/backup/backup_server.sh
3. Once done, navigate to the /backup folder, and open the /backup_server.sh file for editing (for example, with nano):
cd backup nano backup_server.shÂ
Paste the following code inside the file:
#!/usr/bin/env bash NAMEDATE=`date +%F_%H-%M_%s`_`whoami` mkdir ~/backup/$NAMEDATE -m 0755 mysqldump -u dbusername -p"dbpassword" dbname | gzip > ~/backup/$NAMEDATE/db.sql.gz tar czf ~/backup/$NAMEDATE/files.tar.gz ~/public_html chmod -R 0644 ~/backup/$NAMEDATE/* exit 0
The database parameters need to be adjusted:
- dbusername - replace it with the actual database username (weâ$™ve used nctest_production as an example). It can be checked in your websiteâ$™s config file or in the MySQL Databases menu.
- dbpassword - replace it with the actual password for the aforementioned database user. Note that there is no space between -p and the password itself.
- dbname - replace it with the name of the database.
4. Execute the following command to have a cron job created:
(crontab -l ; echo "30 0 * * 1,4 ~/backup/backup_server.sh > /dev/null 2>&1") | sort - | uniq - | crontab -
5. To automatically clean up older backups, add another job:
(crontab -l ; echo "0 0 * * 0 cd ~/backup; find . -type d -mtime +7 -exec rm -rf {} \; >/dev/null 2>&1") | sort - | uniq - | crontab -6. To execute the backup script manually, you can simply run this command via SSH in the folder where the file is stored:
sh backup_server.sh
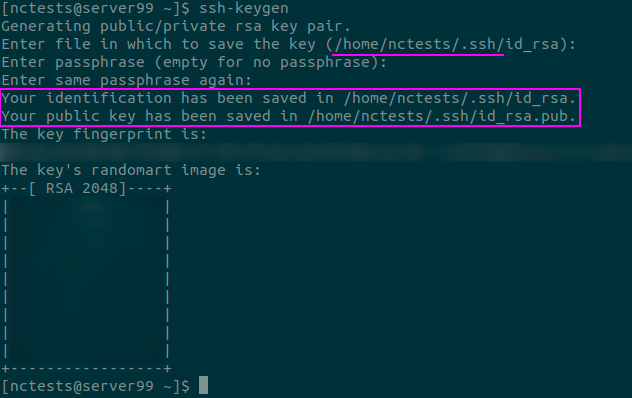
ssh-keygen
3. You will be prompted for the name of the key first. We will leave it blank for this example, and a default id_rsa key will be created in this case, however, you can select a custom name for your key if you already use the id_rsa key for some other purpose (Please note that you will need to prepend your key with a path to the .ssh folder, as highlighted on the screenshot below).
You have now successfully created a pair of keys:
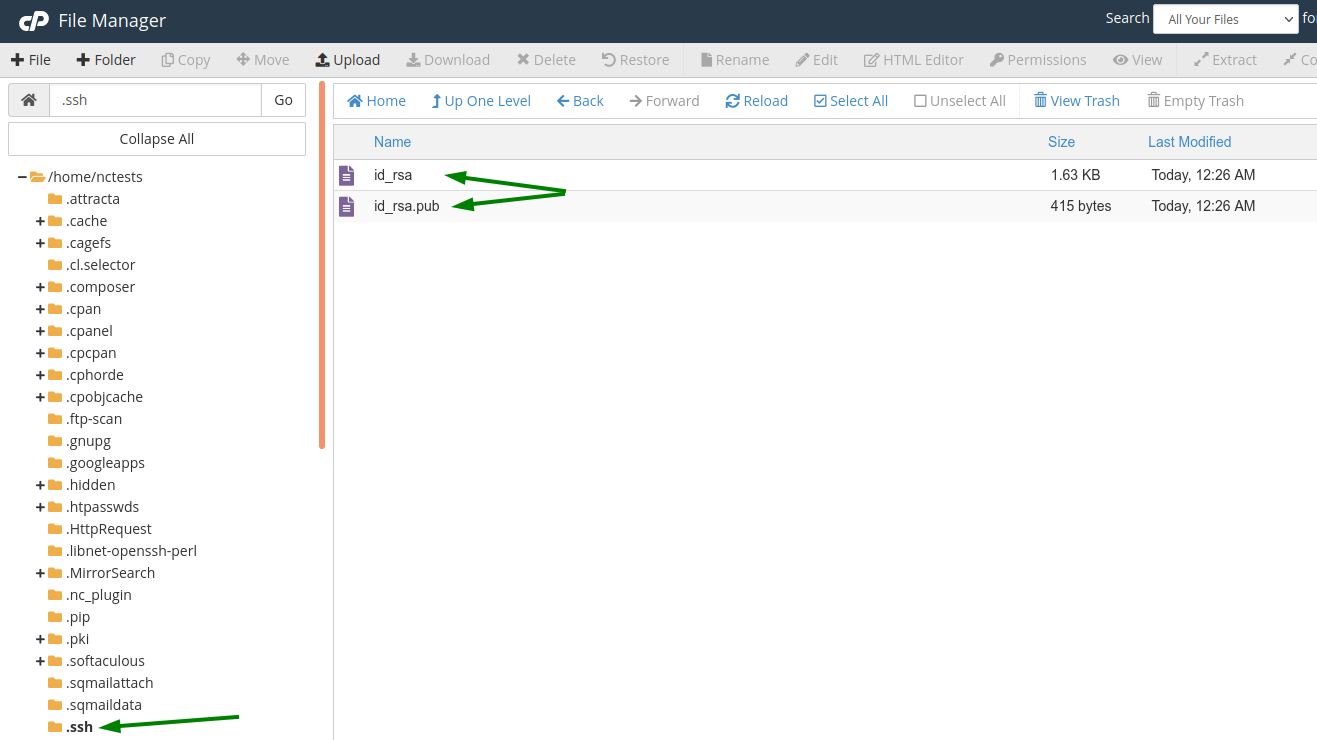
The next step is to authorize the public key (id_rsa.pub) to allow access to your cPanel. You can do it from the "SSH Access" menu in your cPanel:
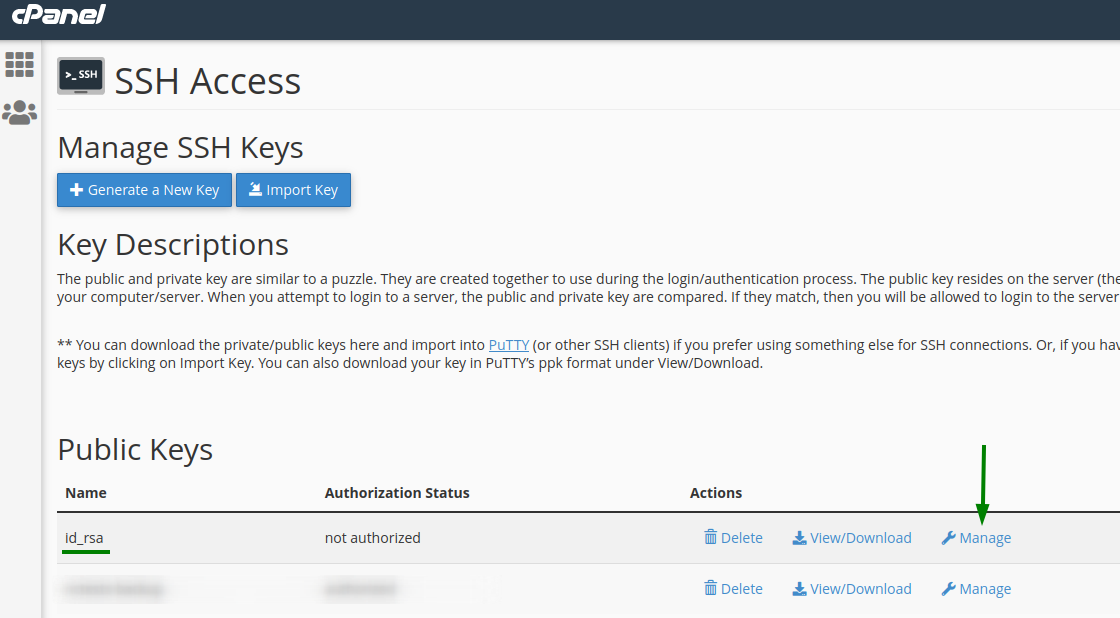
4. Click the Authorize button to authorize the key.
- PuTTY should be installed on your machine to the default path (Program Files).
- You should have your private SSH key converted to a PPK format (the one PuTTY understands) and stored locally. This key should not have a passphrase.
- You should connect to your account via SSH at least once so PuTTY remembers the serverâ$™s fingerprint. Otherwise, the backup script will fail.
Pick a directory on your computer or laptop to store the backups, create a TXT file (you can use Notepad) called backup_client.bat inside the directory. Then, paste the following content into the file:
@ECHO OFF
SET PATH=â$%PROGRAMFILES%â$\PuTTY;%PATH%
SET PKEY=\path\to\private\key.ppk
>backup_client.temp plink.exe -i %PKEY% -t -P 21098 username@servername "ls -thl ~/backup | grep ^d | head -n 1 | awk '{print $9}'"
FOR /f "delims=" %%x IN (backup_client.temp) DO SET DTNM=%%x
pscp.exe -q -scp -batch -r -i %PKEY% -P 21098 username@servername:/home/username/backup/%DTNM% .
del /f backup_client.tempYou will need to modify some parameters to match your local environment:
- Replace the \path\to\private\key.ppk with the actual value, including the .ppk file extension (weâ$™ve used C:\Users\user\private.ppk as an example).
- username and servername are to be changed to the actual ones throughout the script.
- If PuTTY is installed to a non-default path, change %PROGRAMFILES%\PuTTY to the actual directory.
In order to manually start the execution of the script and download the backup, simply run the backup_client.bat file.
To execute the script automatically at a given time, weâ$™ll use the Task Scheduler app. To open it, either search for it in the Start menu or execute the following command via the Run menu:
C:\Windows\System32\taskschd.msc
Once opened, click on Create Basic Taskâ$¦ in the Actions menu:
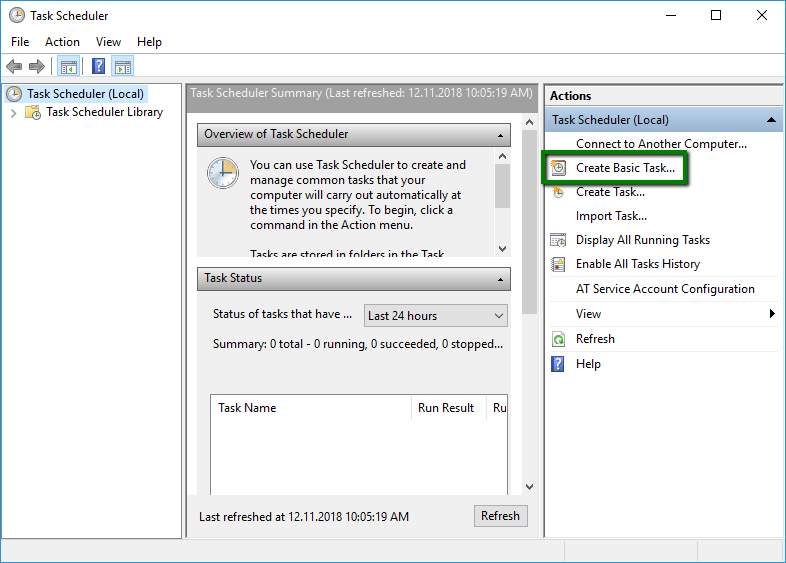
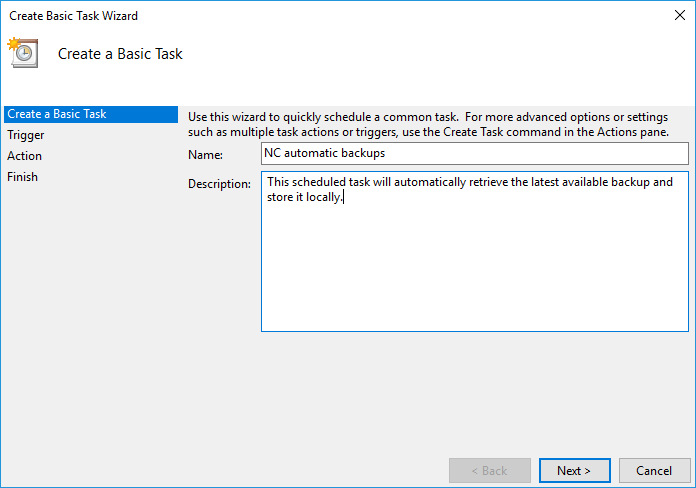
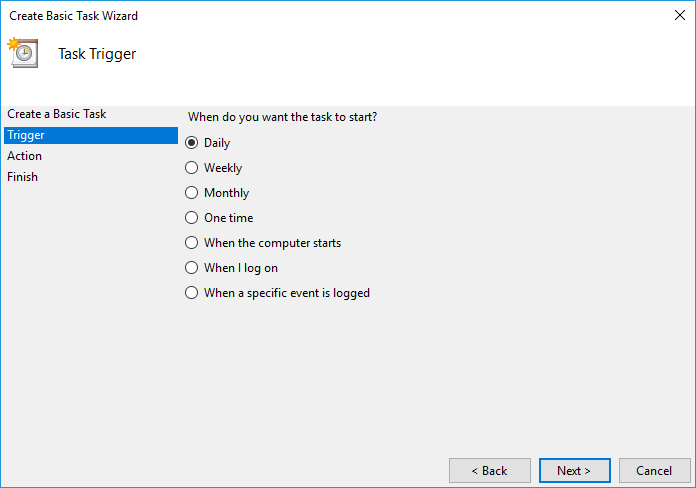
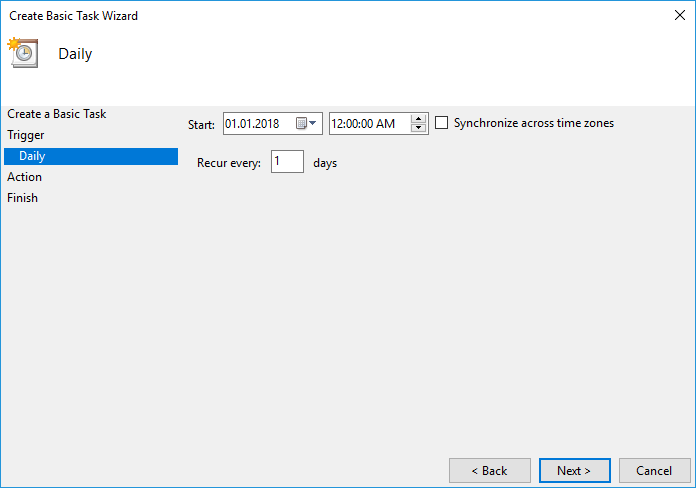
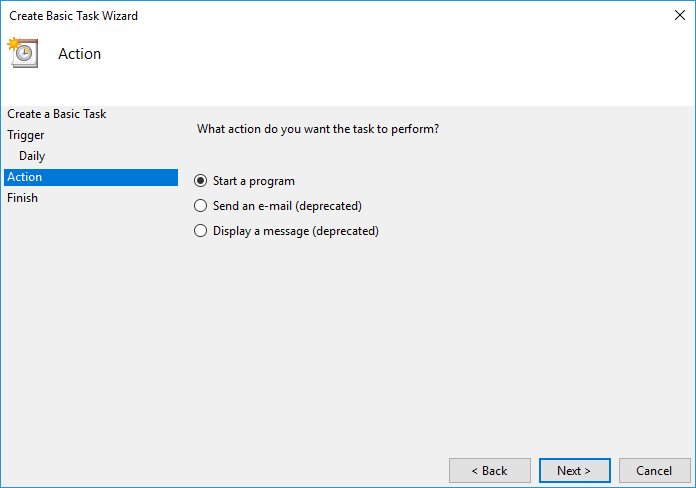
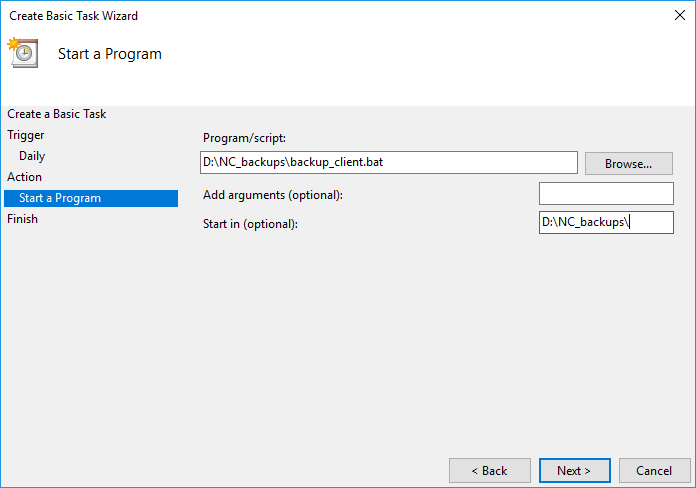
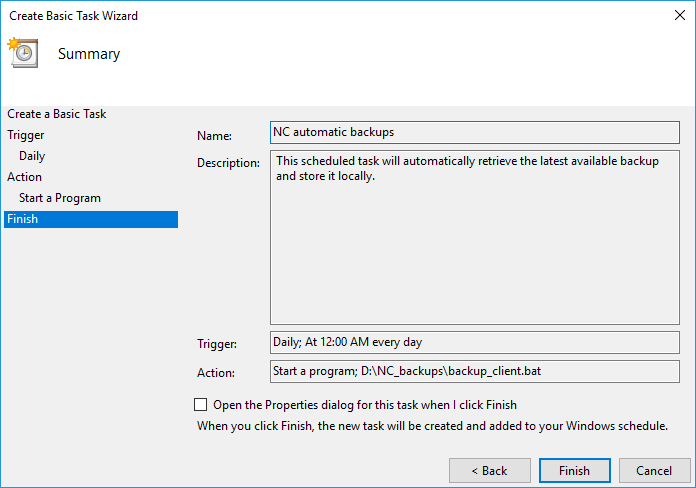
It is also worth noting that a blank command prompt window will appear when the task is executed and will automatically close when it is done.
NOTE: All scripts included in this article are provided for your reference only and come with absolutely no warranty. Use these at your own discretion, as we cannot be responsible for damages.
#!/usr/bin/env bash
ssh -i ~/.ssh/id_rsa -t -p21098 username@servername "ls -thl ~/backup" > backup_client.temp 2>&1
scp -r -i ~/.ssh/id_rsa -P 21098 username@servername:~/backup/`grep ^d backup_client.temp | head -n 1 | awk '{print $9}'` .
rm -f backup_client.tempReplace username with your cPanel username, and servername with the full name of the server your account is hosted on (weâ$™ve used server99.web-hosting.com as an example). If your private key is located in a different place, donâ$™t forget to adjust the path.

The script will download the latest generated backup file.
Once the details are filled, save the file and make sure it has executive permissions. You can use any capable file manager:
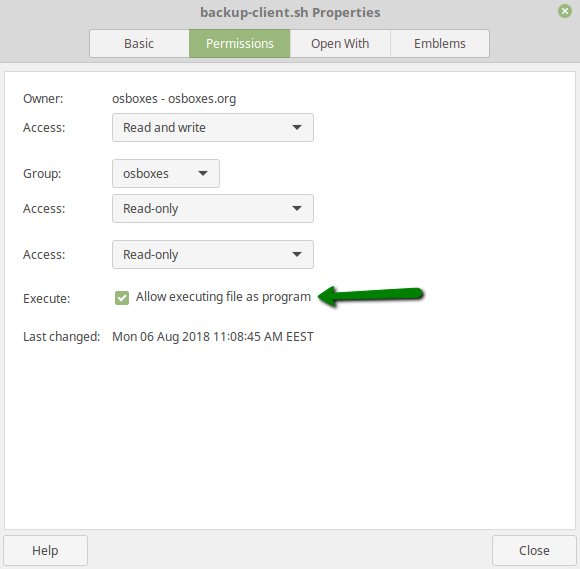
Or you can use the Terminal:
chmod +x ~/backup/backup_client.sh
Now, when the script is invoked, it will list the contents of the /backup folder on the server, find the most recent backup, and download the websiteâ$™s database and compressed files. Please note that the script will fail if the /backup directory on the server is empty.
You can automate the backup retrieval by creating a cron job on your local machine. To do this, run the following command in your Terminal:
(crontab -l ; echo "30 1 * * 1,4 /path/to/backup/dir/backup_client.sh > /dev/null 2>&1") | sort - | uniq - | crontab -
Replace the /path/to/backup/dir/backup_client.sh with the actual path to the backup script. This particular Cron will run every Monday and Thursday at 01:30 AM if your local machine is powered on. Please keep in mind that your local time zone may differ from the server one and adjust it accordingly.
NOTE: All scripts included in this article are provided for your reference only and come with absolutely no warranty. Use these at your own discretion, as we cannot be responsible for damages.
Categories
- cPanel Question 47
- cPanel Software Management 29
- cPanel Tutorials 13
- Development 29
- Domain 13
- General 19
- Linux Helpline (Easy Guide) 156
- Marketing 47
- MySQL Question 13
- News 2
- PHP Configuration 14
- SEO 4
- SEO 42
- Server Administration 84
- SSL Installation 54
- Tips and Tricks 24
- VPS 3
- Web Hosting 44
- Website Security 22
- WHM questions 13
- WordPress 148
Subscribe Now
10,000 successful online businessmen like to have our content directly delivered to their inbox. Subscribe to our newsletter!Archive Calendar
| Sat | Sun | Mon | Tue | Wed | Thu | Fri |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | |
| 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 |
| 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 |
| 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 |
| 28 | ||||||
Recent Articles
-

Posted on : Sep 17
-

Posted on : Sep 10
-

Posted on : Aug 04
-

Posted on : Apr 01
Tags
- ts
- myisam
- vpn
- sql
- process
- kill
- tweak
- server load
- attack
- ddos mitigation
- Knowledge
- layer 7
- ddos
- webmail
- DMARC
- Development
- nginx
- seo vpn
- Hosting Security
- wireguard
- innodb
- exim
- smtp relay
- smtp
- VPS Hosting
- cpulimit
- Plesk
- Comparison
- cpu
- encryption
- WHM
- xampp
- sysstat
- optimize
- cheap vpn
- php-fpm
- mariadb
- apache
- Small Business
- Error
- Networking
- VPS
- SSD Hosting
- Link Building
- centos
- DNS
- optimization
- ubuntu